GERD Causes, Symptoms, and Workable Treatment Alternatives
Millions of people worldwide suffer with the frequent digestive condition known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It happens when irritation and pain result from stomach acid moving back into the oesophagus. While acid reflux on sometimes is acceptable, persistent or frequent reflux might be a sign of GERD, a medical problem.
We'll explore the causes, signs, and available therapies for GERD in this blog so you may take charge of your disease.
Causes of GERD
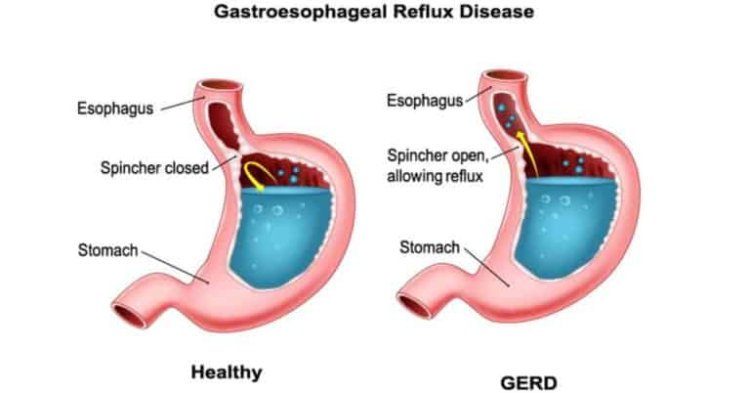
GERD usually manifests as abnormal relaxation or weakening of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a ring of muscle that serves as a valve between the stomach and the esophagus. This makes it possible for stomach acid to irritate and inflame the esophagus by rising back there. The following can be among the contributing causes to the GERD development:
- A Hiatal Hernia is a condition in which a portion of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm into the chest, therefore impairing the LES's ability to function.
- Dietary Factors: Spicy foods, citrus fruits, tomatoes, caffeine, alcohol and fizzy drinks are among the foods and drinks that can either cause or worsen GERD symptoms.
- Obesity : Being overweight might put pressure on the abdomen and raise the chance of GERD.
- Smoking: GERD symptoms might be exacerbated and the LES weakened by tobacco usage.
- Pregnancy : Some women may experience GERD symptoms during pregnancy due to hormonal changes and increased pressure on the abdomen.
Symptoms of GERD
GERD symptoms can be a variety and may differ in intensity from person to person. Not uncommon symptoms consist of:
1. A burning sensation in the chest, heartburn frequently happens after meals or while lying down.
- Regurgitation : Backing up of sour or bitter liquid into the mouth or throat.
- Difficulty Swallowing : Also called dysphagia, this symptom might be brought on by esophageal constriction or inflammation.
- Chronic Cough : A cough brought on by GERD can get worse at night or after meals.
- Sore or Hoarse Throat : esophageal irritation brought on by stomach acid refluxing into the throat.
- Chest discomfort : A medical practitioner should assess chest discomfort linked to GERD as it can resemble heart attack symptoms.
Treatment Options for GERD
Combining food and lifestyle changes with, occasionally, medication or surgical procedures, is usually the best way to treat GERD. Following are some GERD management techniques:
- Lifestyle Adjustments :
- Eat and exercise to keep a healthy weight.
- Raising the head of your bed will help to avoid reflux at night.
- Don't bend over or lay down right away after eating.
- Give up smoking and drink in moderation.
- Dietary Adjustments :
- Recognize and stay away from foods that aggravate GERD symptoms.
- Eat more often, smaller meals to ease stomach discomfort.
- To help with digestion, chew meals slowly and completely.
- Medications :
- Acid reflux and heartburn can be momentarily relieved with over-the-counter antacids.
- Usually recommended to lower stomach acid production and relieve symptoms are proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and H2-receptor antagonists.
- Surgical Interventions :
- To strengthen the LES and stop reflux in severe cases of GERD that do not respond to conventional therapies, surgical procedures like fundoplication may be advised.
CONCLUSION
If GERD is not treated, it can seriously lower quality of life. Through knowledge of the GERD causes, symptoms, and available treatments, people can take proactive measures to efficiently control their symptoms. GERD-related problems can be lessened and symptoms can be managed with medication, dietary adjustments, and lifestyle changes. For accurate diagnosis and therapy, see a medical practitioner if you have severe or ongoing GERD symptoms.
What's Your Reaction?


















